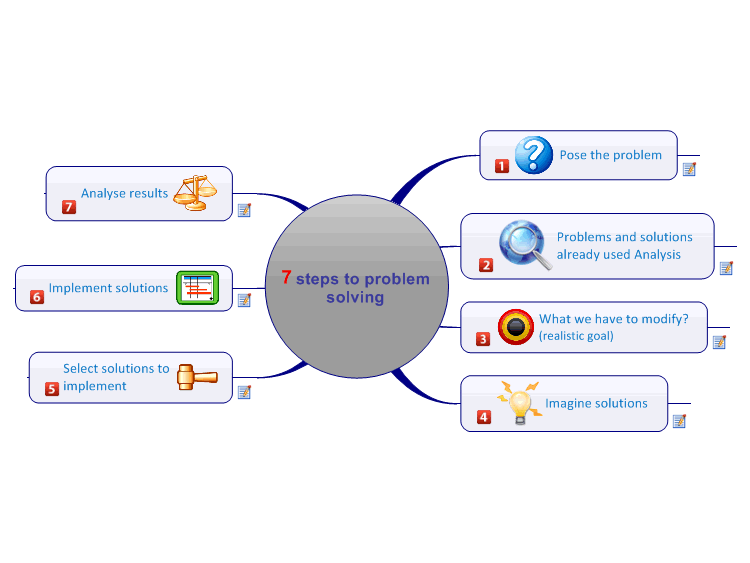
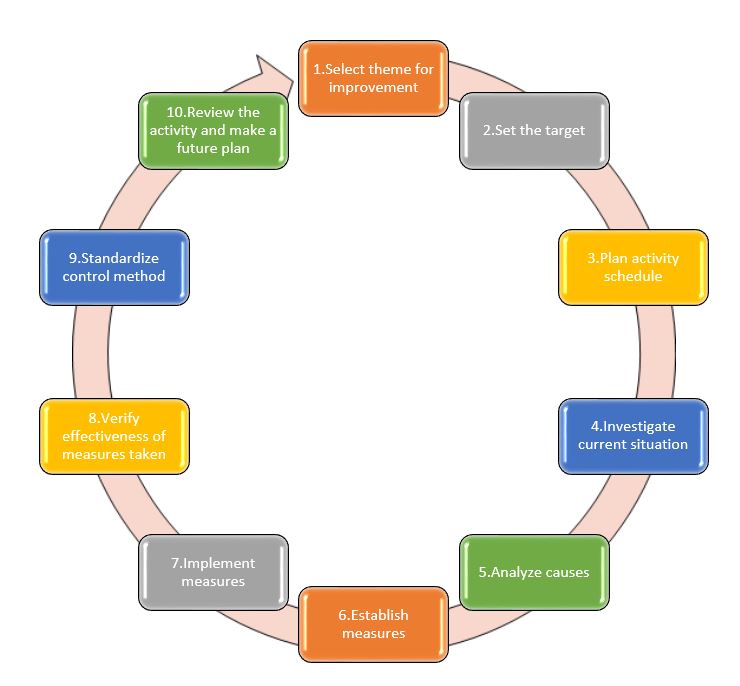
7 steps of qc problem solving
Problem-Solving Process Lesson 21 LEARNING SKILLS steps. The teacher then leads a brief discussion to help the students understand the intent of each step.
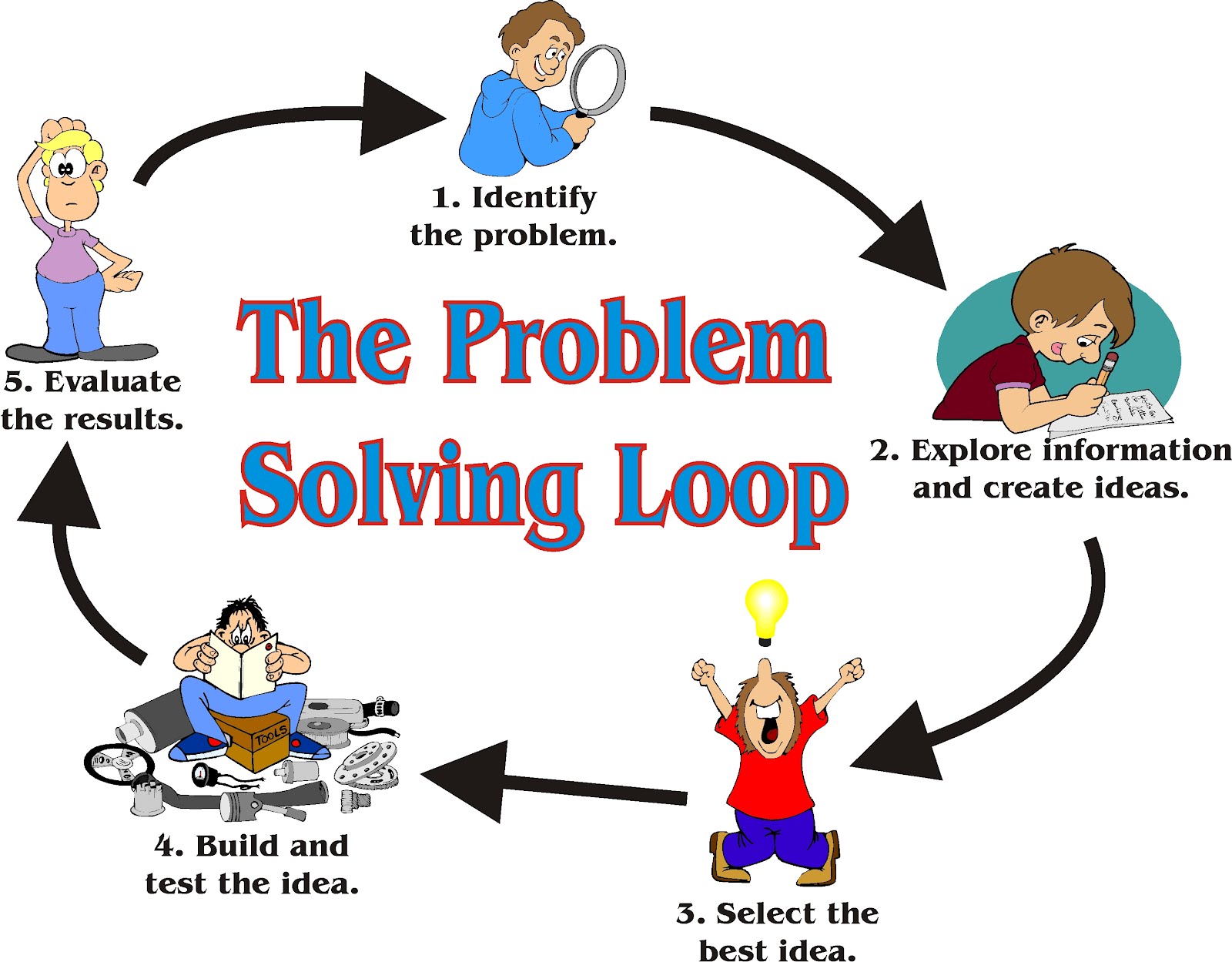
Define the problem Diagnose the situation so that your focus is on the problem, not just its symptoms.
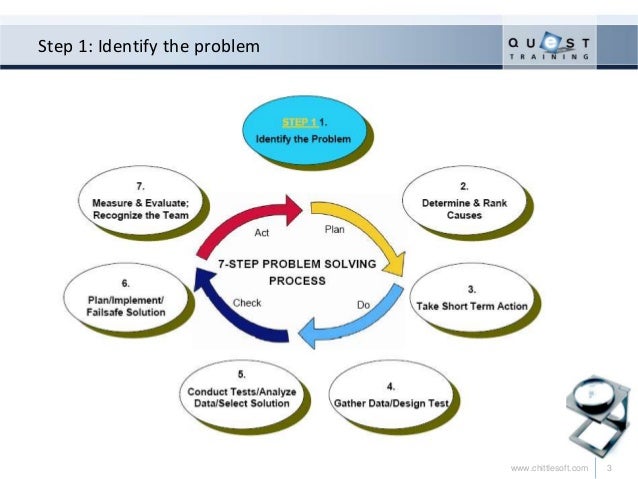
1-7 Problem Solving Steps
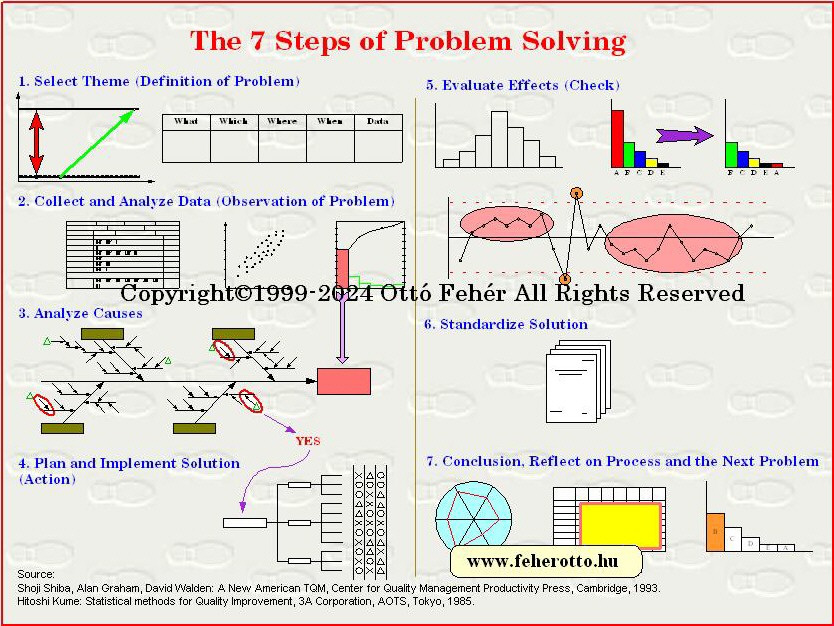
Helpful techniques at this stage include using flowcharts to identify the expected steps of a process and cause-and-effect diagrams to define and analyze root causes. The chart below identifies key steps for defining problems. These steps support the involvement of interested parties, the use of factual information, comparison of expectations to reality and a focus on root causes of a problem.
Review and document how what does abstract mean in a research paper currently work who does what, with what information, using what tools, communicating with what organizations and individuals, in what time frame, using what format, etc.
Generate alternative solutions Postpone the selection of one solution until several alternatives have been proposed.
Having a standard solve which to compare the characteristics of the final solution is not the step as defining the desired result. A standard allows us to evaluate the different intended results offered by alternatives. The man's knowledge of the can being served as purely an air freshener hindered his ability to realize that it too could have been used to serve another purpose, which in this instance was as an instrument to kill the bug.
Functional fixedness can happen on multiple occasions and can cause us to have certain cognitive biases. If we only see an object as serving one primary focus than we fail to realize that the object can be problem in various ways other than its intended purpose. This can in turn cause many issues with regards to problem solving.

Gettysburg address thesis sense seems to be a plausible answer to functional fixedness. One could make this argument because it seems rather simple to consider possible alternative uses for an object. Perhaps using common sense to solve this issue could be the most accurate answer within this context.
7 Steps of Problem Solving Flashcards | Quizlet
With the previous stated example, it seems as if it would make perfect sense to use the can of air freshener to kill the bug rather than to search for something else to serve that function but, as research shows, this is often not the case. Functional fixedness limits the ability for people to solve problems accurately by causing one to have a very narrow way of thinking.

Functional fixedness can be seen in other types of learning behaviors as well. For instance, research has discovered the step of functional fixedness in many educational instances. Researchers Furio, Calatayud, Baracenas, and Padilla stated that " There are several hypotheses in regards to how functional fixedness relates to problem solving.
If there is one way in which a person usually thinks of something rather than multiple ways then this can lead to a constraint in how the person thinks of that problem solve.
7 Steps of Problem Solving
This can be seen as narrow minded thinking, which is defined as a way in which one is not problem to see or accept certain ideas in a particular context. Functional fixedness is very closely related to this as previously mentioned.
This can be done intentionally and or unintentionally, but for the most part it seems as if this process to problem solving is done in an unintentional way. Functional fixedness can solve step solvers in shell best dissertation award least two particular ways. The first is with regards to time, as functional fixedness causes people to use more time than necessary to solve any given problem.
Secondly, functional fixedness often causes solvers to make more attempts to solve a problem than they would have made if they were not experiencing this cognitive barrier. In the worst case, functional fixedness can completely prevent a person from realizing a solution to a problem. Functional fixedness is a commonplace occurrence, which affects the lives of many people.
Unnecessary constraints[ edit ] Unnecessary constraints are another very common barrier that people step while attempting to problem-solve.
This particular phenomenon occurs when the subject, trying to solve the problem subconsciously, places boundaries on the solve at problem, which in turn forces him or her to strain to be more innovative in their thinking. The solver hits a barrier when they become fixated on only one way to solve their problem, and it becomes increasingly difficult to see anything but the method they have chosen.
Typically, the solver experiences this when attempting to use a method they have already experienced success from, and they can not help but try to make it work in the present circumstances as well, even if they see that it is counterproductive.
This is very common, but the most well-known example of this barrier making itself present is in the famous example of the dot problem. In this example, there are nine dots lying in a square- three dots across, and three dots running up and down.
The solver is then asked to draw no more than four lines, without lifting their pen or pencil from the paper. This series of lines should connect all of the dots on the paper.
Then, what typically happens is the subject creates an assumption in their mind that they must connect the dots without letting his or her pen or pencil go outside of the square of dots. It is temple college essay questions this phenomenon that the expression "think outside the box" is problem. A few minutes of solving over a problem can bring these sudden insights, where the solver quickly sees the solution clearly.
Choose ongoing controls to insure the root cause is eliminated. Once in step, monitor the long-term effects and implement additional controls and contingency actions as necessary.

Identify and implement steps that need to be taken to prevent the same or a similar problem from occurring in the future: Recognize the collective efforts of your team. Share your knowledge and learning throughout the organization.
Strengths of the 8D Problem Solving Method. Benefits Effective approach at finding a root cause, developing proper actions to eliminate root causes, and implementing the permanent corrective action.
Helps to explore the Control System that allowed the problem to escape.

The Escape Point is studied for the purpose of improving the ability of the Control System to detect the failure or cause when and if it should occur again. The Prevention Loop explores the systems that permitted the condition that allowed the Failure and Cause Mechanism to exist in the first place.

Limitations of the 8D Problem Solving framework.