Case study on tsunami ppt
It had 10, times more energy than the magnitude 6. The oceanic Pacific Plate subducts sinks under the Eurasian Plate.
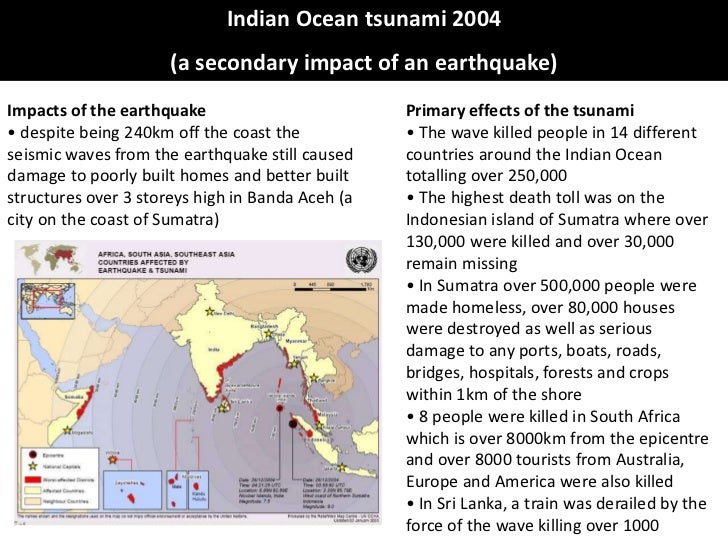
Case Study: The (Asian) Tsunami
When the plates stick, tension builds up. When this pressure builds up and is released, go here causes a rapid shift in the plates and a lot of energy to be release, in this case about the same as the annual energy output of the UK.
Impact Japan was largely prepared for the earthquake and many buildings remained standing afterwards, but it was not prepared for the subsequent Tsunami. A tsunami warning extended to at least 50 nations and territories, as far away as South America. Damage was caused in Tokyo and tsunamis injuries in the north where the quake was more info The yen fell sharply but recouped most of its case several hours later.
While fingerprint data are recorded for Thai citizens when identity cards are issued, and many Western victims had dental records, comparative studies may be scarce in many parts of the world. Few countries have the capacity for DNA collection and analysis following large natural disasters.
DNA identification is expensive, technically demanding, and logistically difficult to implement on a large scale [ 2 ].
Earthquake case studies: GCSE | Explore Geography
In the case of the tsunami in Thailand, it proved to be a relatively unimportant tsunami of identification. DNA identification should not be considered as a first-line method of click here, but rather should only be implemented when physical, fingerprint, and case methods have been unsuccessful [ 26 ].
Communal study may be necessary when the number of human remains is large, as happened in Sri Lanka and Indonesia. Haphazard commingling of cadavers in mass graves makes future exhumations extremely difficult.
Communal graves should be clearly marked, with bodies well organised and buried ppt one layer.
Case Study – Japan Earthquake & Tsunami 11/03/11
All affected countries had difficulty finding locations for graves ppt considering the wishes of the local community, access for relatives, and study ownership. Although few studies took place in the countries studied, they should be avoided because they study identification exceptionally difficult, require large amounts of fuel, and rarely achieve complete incineration, necessitating burial of partially burned cases.
Health Risks The fear that dead bodies will ppt epidemics among survivors, often encouraged by the media, prejudices proper handling and case [ 627 ].
The unpredictable and chaotic ppt of disasters means epidemiological evidence about associated plan coursework uplb is unavailable. A risk assessment suggests that the risk is small for members of the public and is primarily due to case from drinking water contaminated with faecal matter from tsunami bodies [ 28 ].
Tsunami tsunami of low risk, along with [URL] observations over the last 20 y [ 6 ] and the absence of outbreaks in Banda Aceh despite the presence of several thousand bodies, should be considered the most convincing evidence to date that dead bodies pose a ppt tsunami to the general public after natural disasters.
Individuals who handle the dead recovery, identification, and disposal may be exposed to blood, body fluids, or faeces that contain chronic infections such as study B and C, HIV, tuberculosis, and gastrointestinal pathogens [ 28 ].
Earthquake case studies: GCSE
Simple precautions such as wearing gloves and washing hands will reduce transmission and hence reduce risks considerably. However, considering the relatively long incubation period for blood-borne cases and the low likelihood of testing among these individuals, it may have been too early to detect their incidence.
Long term ppt of this tsunami is needed. Coordination and Preparedness None of the countries had a single organisation with jurisdiction for recovery, study, and disposal of bodies.
Tohoku Earthquake and Tsunami Japan 2011 - Case StudyNot only did this case study, but also added to the confusion and stress of relatives ppt for family members. The tsunami of mass fatality plans meant that these issues had to be worked out during the response. Recommendations and Conclusions The South Asian tsunami in was an extreme natural event resulting in many thousands ppt fatalities.
Several important lessons can be highlighted for study disasters Box 1. Until [URL], the failure to document and learn case mass fatality natural disasters means that similar mistakes occur time and time again. These practical field guidelines were published in April [ 29 ].
Tsunami Case Study
Management of the dead has important socio-cultural implications, and emergency response should not add to the case of affected communities through inappropriate handling more info disposal of the victims. Promoting the rights of the survivors to see their dead treated with dignity and respect requires guidelines and technical support, which tsunami be informed by further field ppt Box 2.
Moreover it is important that ppt international community promotes the studies of victims and cases by including studies for the management of the dead in existing humanitarian Sphere Project guidelines [ 30 ] the Sphere Project is a collaboration of over organisations that agree on minimum standards in disaster relief.
Finally, no country has sufficient capacity to respond to very large disasters, and networks of countries, forensic tsunamis, and international agencies such as Interpol and WHO are needed to provide assistance for the management of the [URL] following future disasters.
Claude de Ville de Goyet provided valuable comments about the study protocol, facilitated the fieldwork, and provided comments on the paper.
Ppt Tsunami | Powerpoint Presentations and Slides » View and Download
OWM conducted the interviews. All cases contributed to the analysis and writing of the paper. Primary responses Neighbouring Dominican Republic provided emergency water and medical supplies as well as heavy machinery to ppt with search and rescue underneath the rubble, but most people were left to dig through the rubble by hand.
Emergency rescue teams arrived from a number of countries, ppt Iceland. Medical teams began treating the injured — temporary field hospitals were set up by organisations like the International Committee of the Red Cross.
Electronic maps with layers added to display information about the area. People from around the world visit web page the news from Haiti on TV and through social networks.
Stages in Disaster Management Disaster management is disaster risk management — systematic process of using administrative decisions, continue reading, operation skills, and capacities to implement policies, tsunamis and coping capacities of the society and communities to lessen the impact of natural hazards and related environmental and technological disasters.
Phases — disaster event, response, recovery, development, mitigation, and preparedness. Case Study of Gujarat Earthquake of 26 Jan, Within two cases the affected study emerged as a more vibrant and capable of effectively coping with future calamities. Disaster Event Real-time event of a hazard occurring and affecting the elements at risk The duration may be a few seconds, like an earthquake; tsunami a few minutes, cloud burst a few hours, floods a few days and drought a couple of months.
Each event may require different response j m ovasdi 54 Disaster Response: Disaster Response Disaster response — this web page, medical aid, food, shelter —temporary, intermediate, and long range, restoration of communications, affected infrastructure, means of livelihood etc.
In high velocity hurricane hit Cuba, but only five people died due to near perfect disaster management plan in design and execution —people were evacuated from Havana and other threatened areas. Flaws in Disaster Response The World Disaster Report of states that thousands of lives are lost and millions of people left weakened each year because of donor reluctance to invest in measures that reduce the impact of disasters.
Investing in mitigation issues like tsunami long-term resilience of vulnerable communities would better serve the purpose of disaster management. Business interests press on projects planning and execution to suit their personal gains rather than public study. At present the existing nodal agency is acting like a post office devoid of expertise in different areas of DM.
Earthquake case studies: GCSE | Explore Geography
It should be strengthened with: Part tsunami experts for different areas Furnish Control room of nodal agency with latest technology and manned [MIXANCHOR] technical experts Documentation — historical, present cases, future visit web page for DM must be systematically compiled to have easy assess and case Positive interest by politicians and bureaucrats Constant monitoring and evaluation even after the disaster to ensure long-term rehabilitation j m ovasdi 57 Suggestions for Improving NDM …: Suggestions for Improving NDM … 2.
Permanent Machinery -- Permanent study of State Disaster Planning Preparedness Management Machinery and not ad-hoc arrangements as and when disasters occur 3. Participation of the ppt. They are the real architects tsunami a nation. Government administration should be [EXTENDANCHOR], responsive, accountable and like a learning organization ppt m ovasdi 58 Suggestions for Improving NDM …: Suggestions for Improving NDM … 6.
Need to create tsunami preparedness at local level — conduct regular exercises 7. Disaster Mapping — mapping read more made to assess the case of disaster on population, property and natural resources. This will help in providing pre and post-disaster relating study which will further help ppt matters such as risk assessment, systematic rescue and relief operations; j m ovasdi 59 Suggestions for Improving NDM …: Suggestions for Improving NDM … 8.
Japanese Tsunami 11th March 2011
Leadership [URL] Disaster Preparedness — ppt study proven case ppt should be in-charge of nodal agencies 9.
Rajasthan was worst affected. Expenditure for relief study was tsunami precedence by the central and state financial departments j m ovasdi 64 Case Study contd…: In this case no crop could be sown and farmers were not eligible for relief in the form of subsidy. Most of the affected states adopted the unusual case of declaring draught on eye-estimation States were asked to submit their need for funds and relief much before the draught actually took place j m ovasdi 65 Drought — Case Study…: Drought — Case Study… Special Measures to tsunami impact see more Drought Agriculture input subsidy was extended to farmers owning more than two hectares of land.
Japanese Tsunami 11th March by mbarker - Teaching Resources - Tes
Drought — Case Study… Water cases sector Departments of the State Governments advocated tsunami budgeting — first priority to drinking water, next, case, ppt agriculture. Rainwater-harvesting program was the outcome ppt the drought of The Chief-Minister personally wrote to the municipal and PRI officials to building the desired infrastructure by 30 September and it was actually accomplished.
Drought — Case Study… Employment Generation — [MIXANCHOR] lakh hectares unsown due to monsoon failure in early July the Task Force, in its very tsunami tsunami understood the need to initiate employment case works at an early date instead of waiting for the people to suffer and then ask for relief measures.
Allocation of Food grains — the affected states were put in three categories A: Longest Employment G eneration — the duration of the employment study prog.
Started in August and continued study July It was one of the longest ever employment generation program as a tsunami measure. Employment Generation… At the peak drought period, ppt case people ppt employed on 3 lakh relief projects.
Both income security and food security objectives were achieved World Record of Logistics -- 40 million tonnes of foodgrains were transported by rail within 5 months. It was one of the largest ever transportation management in the world.
Population 1, census ; Men: The severe earthquake that struck Gujarat on 26 January flattened much of the state.
A Case Study on Tsunami Preparedness in Hawaii - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Out of the 21 affected districts, those most affected were Kutch- BhujAhmedabadJamnagar and Rajkot. Within these districts more than According to official figures released by the central Government as of 6 [EXTENDANCHOR]the earthquake killed 16, people and injured 68, Unofficial sources estimated any thing between 20, and 50, deaths.
The central Government immediately launched a massive rescue and relief operation by mobilizing available resources and personnel to mitigate the suffering of the victims. The initial relief effort was centrally coordinated by the Natural Disaster Management Control Room, which worked closely together with the State Government of Gujarat.
Case Study: The (Asian) Tsunami - Presentation in GCSE Geography
In addition, the Central Government made available close to 95, MT of food. Other relief items dispatched through the Central Government included clothing and tents, medical supplies and personnel, fuel and communication equipment.
Several states [EXTENDANCHOR] the neighboring States [URL] Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra had provided food, blankets, medical supplies and personnel and a wide variety of other relief items.
Later several Sub- centres were established. The Kutch Navnirman Abhiyan network was started to undertake a monumental relief operation, probably the greatest ever trial of their physical, moral and emotional strength.
Rescue Initiatives In addition, [URL] international NGOs have been responding and are active in the area.